Receptor Occupancy
A receptor occupancy assay measures the degree to which the test drug occupies its target receptor in the tissue or animal. Receptor occupancy is determined by measuring the ability of a dose of the test drug to compete with binding of a radiotracer to the receptor.
Receptor occupancy assays are useful in drug development as they determine the dose or plasma concentration of the test drug needed to reach a therapeutically-effective receptor occupancy level.
Ex Vivo Receptor Occupancy
In this technique the test compound is administered to the animal. The level of receptor occupancy by the test compound is then subsequently measured ex vivo. This is determined by harvesting the tissue at the time of peak drug levels, sectioning the tissue on a cryostat and measuring the degree to which the binding of a radiotracer incubated with the sections is inhibited by bound drug in the sections.
In Vivo Receptor Occupancy
For receptors in which a suitable in vivo radiotracer is available, receptor occupancy by the test compound can be measured directly in vivo. This is achieved by dosing the animal with the test compound followed by intravenous administration of a radiotracer for the targeted receptor. At the time of peak brain or tissue levels of the test drug, the animal is euthanized and the percentage reduction in radiotracer binding to the target receptor resulting from competition with the test compound is measured.
Example Data
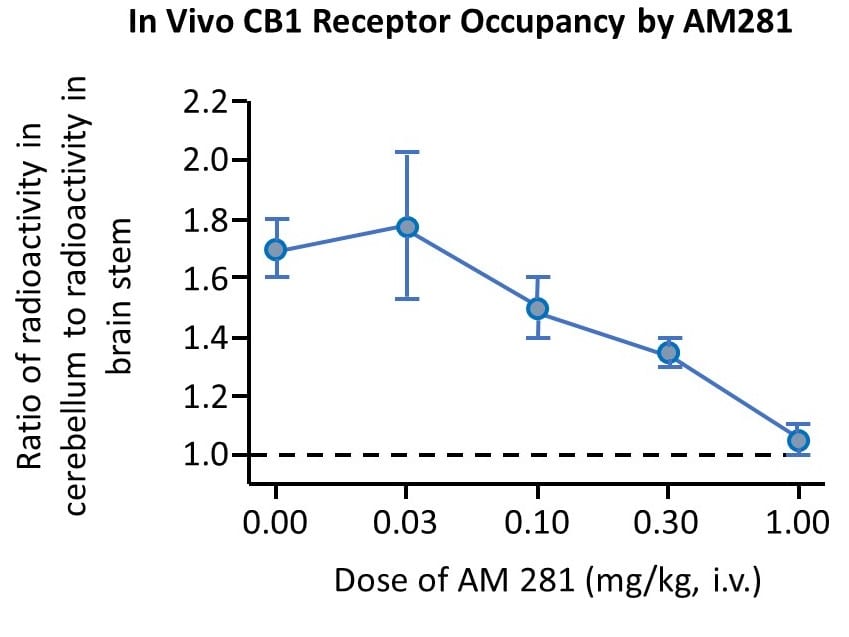
In vivo CB1 cannabinoid receptor occupancy by a cannabinoid drug, as determined by inhibition of the corresponding radioiodinated tracer. Values are ratios of radioactivity in cerebellum (i.e. a CB1 receptor-rich region) to brain stem (a reference region) and are the means of 5 – 6 animals per dose. Unlabeled drug reduced specific radiotracer binding by 50% (~ 50% receptor occupancy) at 0.3 mg/kg. Dotted line indicates the level of non-specific binding.
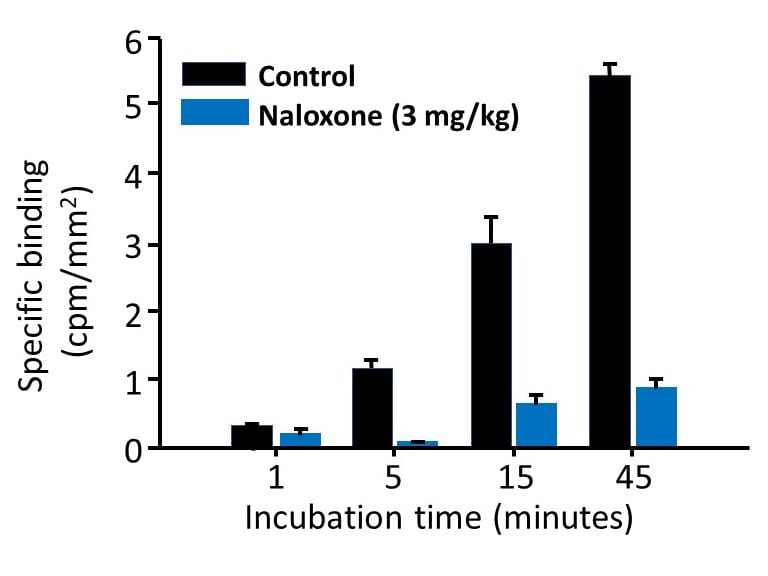
Ex vivo occupancy study: Autoradiographic binding of [3H]DAMGO to striatal sections from a rat that had been given a mu receptor antagonist (3 mg/kg, i.p.) 20 min prior to sacrifice. Incubation time of the sections in [3H]DAMGO is indicated below each bar. Binding is reduced at all incubation time points in the sections from the treated animal due to occupancy of mu receptors in the tissue by the drug.