What are Ligand Binding Assays?
Receptor ligand binding assays are techniques used to study the interaction between a ligand and a target protein (receptor), crucial for identifying and optimizing test compounds by measuring binding affinity and kinetics.
Why are Ligand Binding Assays Essential for Early Stage Drug Discovery?
Receptor ligand binding assays identify compounds with high binding affinity to target proteins. They characterize binding kinetics, providing insights into the rates of association and dissociation, which are important for predicting drug potency and duration of action. Additionally, these assays assess the specificity of ligand binding, aiding the design of compounds that target the desired proteins with minimal off-target effects.
Ligand Binding Assays: Binding Parameters
- Kd. The dissociation constant indicating the affinity of a ligand for a receptor, with lower values reflecting higher affinity.
- Ki. The inhibition constant representing the potency of an inhibitor, with lower values indicating higher potency.
- kon / ka. The rate at which a ligand binds with a receptor to form a complex.
- koff / kd. The rate at which the ligand dissociates from a receptor.
- Bmax. The maximum binding capacity showing the total number of available binding sites in a sample.
- IC50. The concentration of an inhibitor required to reduce a given biological activity by 50%.
- EC50. The concentration of a drug that produces 50% of its maximum effect.
- Emax. The maximum effect achievable with a drug, regardless of dose.
Receptor Ligand Binding Assays: Our Platforms
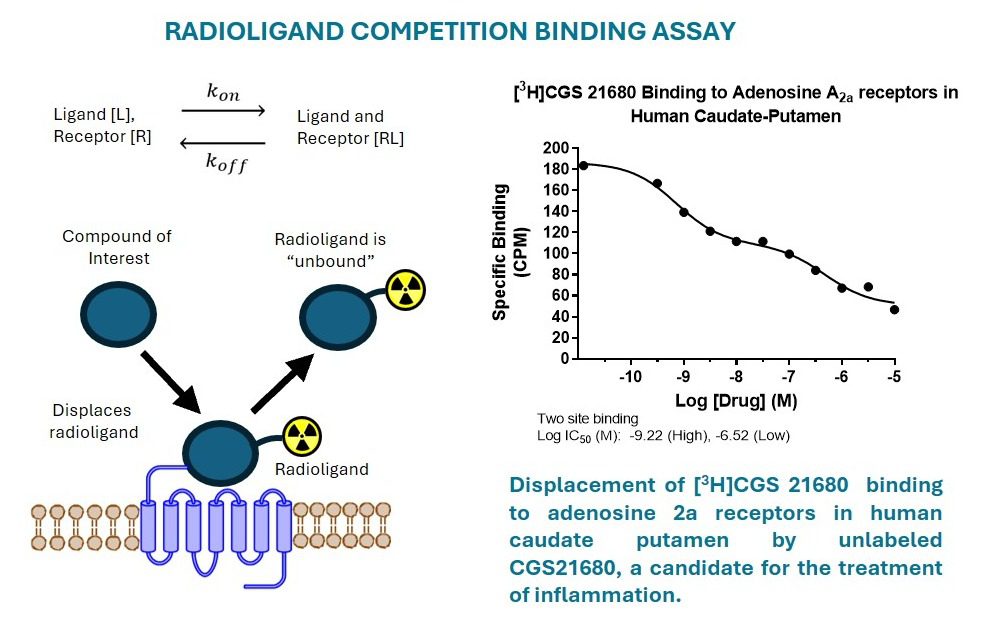
Radioligand Binding Assays
- Radioligands are used to measure ligand binding to native or recombinant receptors. The bound complex’s radioactivity is measured, providing high sensitivity and robust assays.
- Ideal for quantifying ligand binding in a variety of cell and/or tissue types.
- Determine a compounds affinity (Kd) for a receptor or determine the density of receptors in tissue (Bmax).
- Determine the association kinetics (Kon) and dissociation kinetics (Koff) of ligands of interest with the target receptor.
- At Gifford Bioscience, we undertake compound screening, custom iodination of proteins of interest and determination of changes in receptor density in diseases such as cancer or neurodegenerative disease.
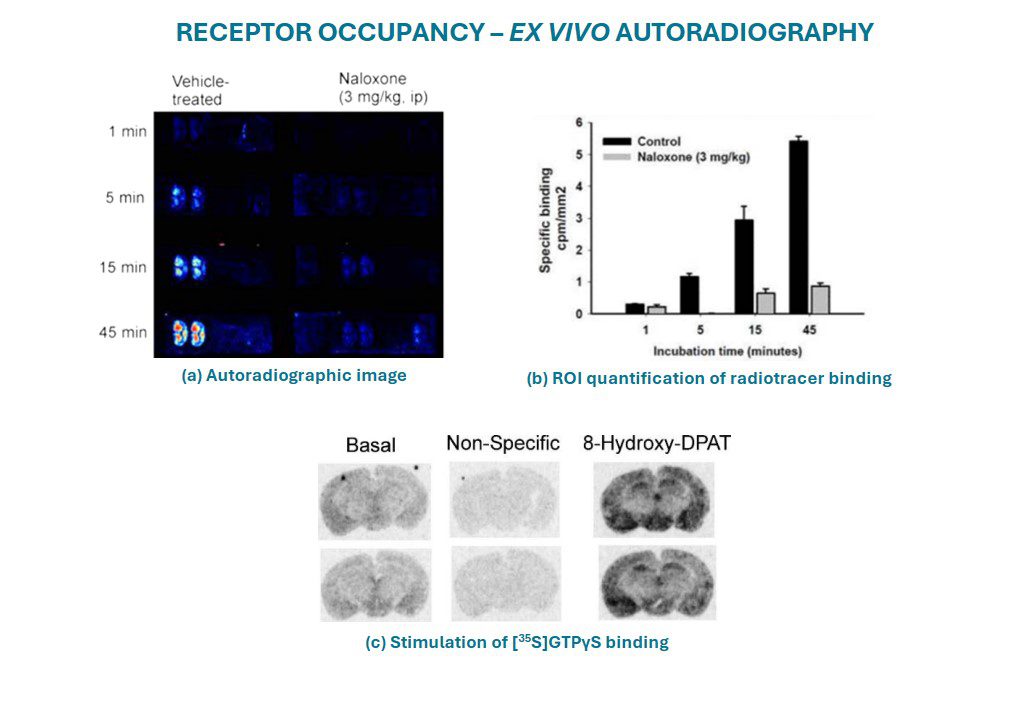
Autoradiography and Receptor Occupancy
- Uses radiolabelled ligands to visualize the distribution of binding sites in tissue sections or cell preparations. The sample is exposed to a phosphor screen or detector, capturing the radiographic image of ligand binding.
- Provides spatial distribution information, useful for studying tissue-specific binding and receptor localization.
- Quantify available binding sites after in vivo drug treatment of the animal to measure receptor occupancy and target exposure to the test drug.
- Identify changes in receptor expression in cancerous tissue.
- Gifford Bioscience has extensive experience obtaining human disease tissue to investigate the interactions of your compounds or target protein.
Click here to
get in touch
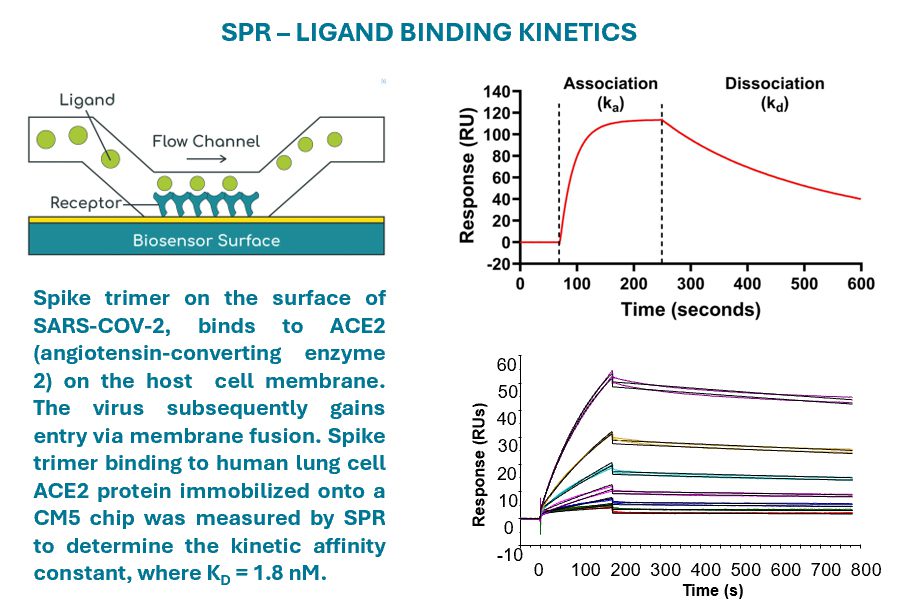
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
- Detects changes in refractive index as ligands bind to a target protein immobilised onto a sensor chip, measuring real-time binding kinetics without labeling.
- Offers detailed kinetic profiles (kon or ka and koff or kd) and real-time analysis.
- Can be used to determine antibody affinity, including monoclonal antibodies for cancer treatment.
- Useful for performing concentration analysis and analyte quantitation in biological samples.
- Provides a label-free method for measuring small molecule test compounds binding to target proteins.
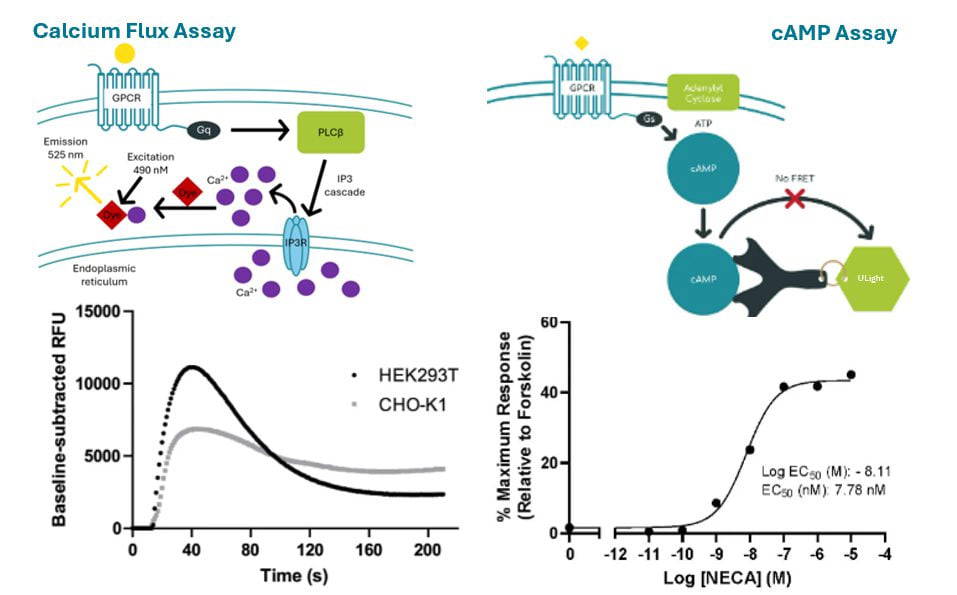
Functional Ligand Binding Assays, Radioimmunoassays (RIAs) and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISAs)
- At Gifford Bioscience, we are able to screen a number of downstream signalling pathways to characterize the functional activity profile of your compounds, allowing you to identify appropriate pathway activation to reduce side-effects.
- Functional ligand binding assays provide information on the potency (EC50 or IC50) and efficacy (Emax) of the drug and on ligand bias.
- Radiometric techniques, fluorescent dyes and antibodies are used to label the signalling output of interest to determine the cellular activity of your ligand, including [35S]GTPγS binding, calcium release, cyclic AMP production and MAP kinase activity.
- RIAs and ELISAs can be used to quantify target proteins released as a consequence of ligand binding or assess receptor cell surface expression.
Leverage our ligand binding assays, including radiometric, SPR, and autoradiography, to accelerate your research in therapeutic areas such as cancer and neurodegenerative disease. With expertise in human and non-human tissues, cells and cell membranes, we provide comprehensive, high-sensitivity analysis and robust data to optimize drug candidates and understand receptor ligand binding interactions. Partner with us to enhance your drug discovery and lead optimization efforts in areas such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
Contact Us
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA. The information you supply will be processed in accordance with the General Data Protection Regulation (EU & UK). For further details, please refer to our Privacy Policy.

Copyright © 2025 Gifford Bioscience Limited
Privacy Policy