Functional Assays
Our functional assay service measures the effect of compounds of interest upon the biological activity of the target. We use both radiometric and fluorescent-based approaches in live immortalized/transfected cell lines as well as primary cell lines, and in some cases on membranes. All of our assays are tailored to your specific needs; your frozen cells/membranes can be sent to us, or alternatively, our customized cell culture and transfection ancillary services are available to you.
We use this technique to:
- Determine EC50 and Emax of agonists;
- Determine IC50 of antagonists;
- Screen compounds to identify full agonists, partial agonists, inverse agonists, antagonists, allosteric modulators and inhibitors.
Radiometric-based Functional Assays
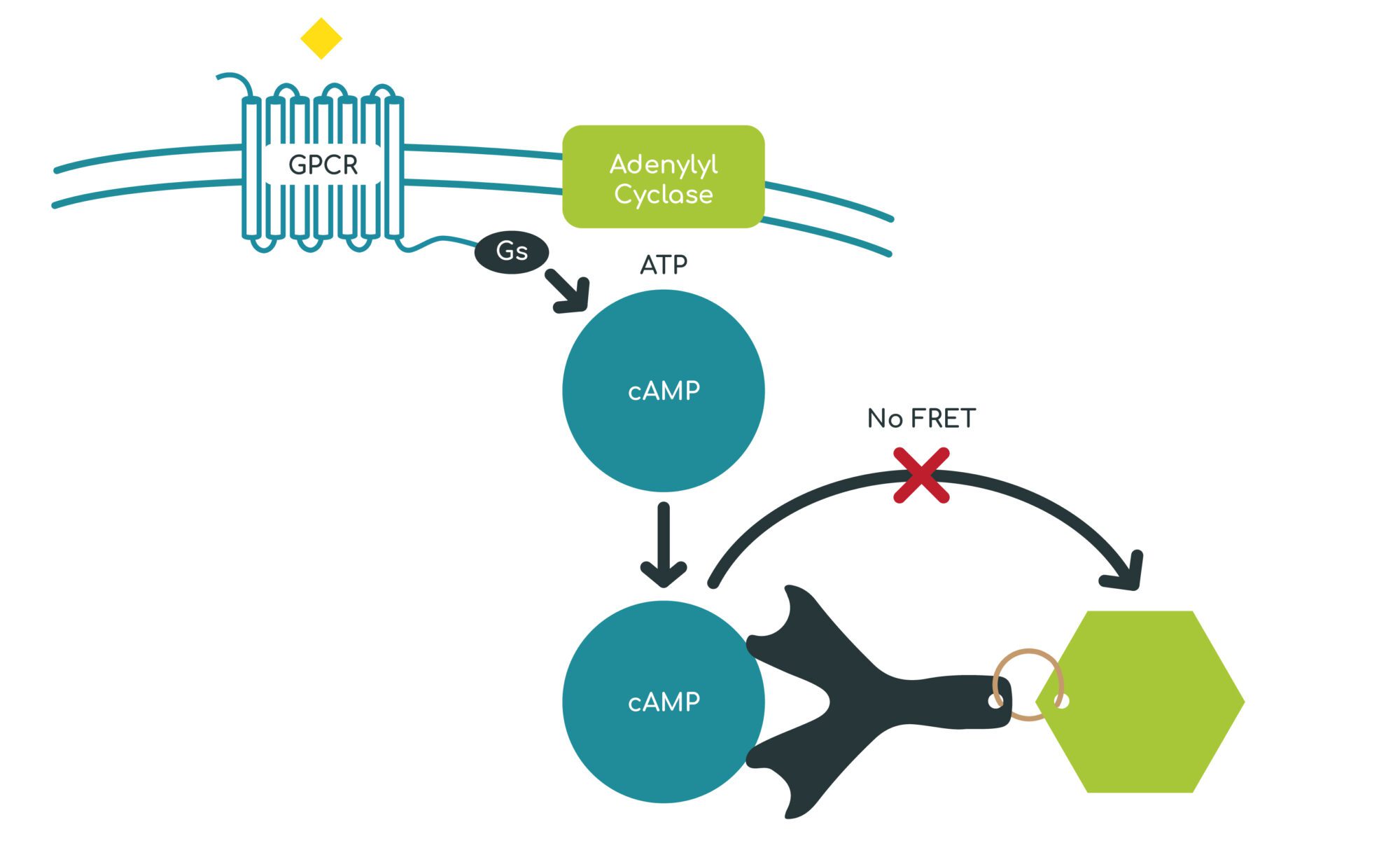
Radioimmunoassays (RIA) can be utilized to measure concentrations of targets in a sample, such as second messenger levels in response to treatment of cells with compounds of interest. Radiolabeled antigen competes with unlabeled antigen for binding sites on an antibody specific to the antigen. As concentrations of unlabeled antigen increase, more of the radiolabeled tracer is displaced, and bound radioactivity decreases. [125I]cAMP RIA is used to measure changes in cellular cAMP levels resulting from activation of GPCRs coupled to Gs and Gi/o. cAMP levels are measured in cell lysates via competition
[35S]GTPγS assays measure G-protein activation as a result of an agonist occupying the associated GPCR. GDP dissociates from the Gα subunit and is replaced by GTP. In the GTPγS assay, non-hydrolysable [35S]GTPγS binds to the Gα subunit and bound radioactivity can then be quantified. In particular, activation of the more abundant Gi/o-coupled receptors can be investigated. With an addition immunoprecipitation step, activation of Gs and Gq-coupled receptors can be measured.
Fluorescence and TR-FRET-based Functional Assays
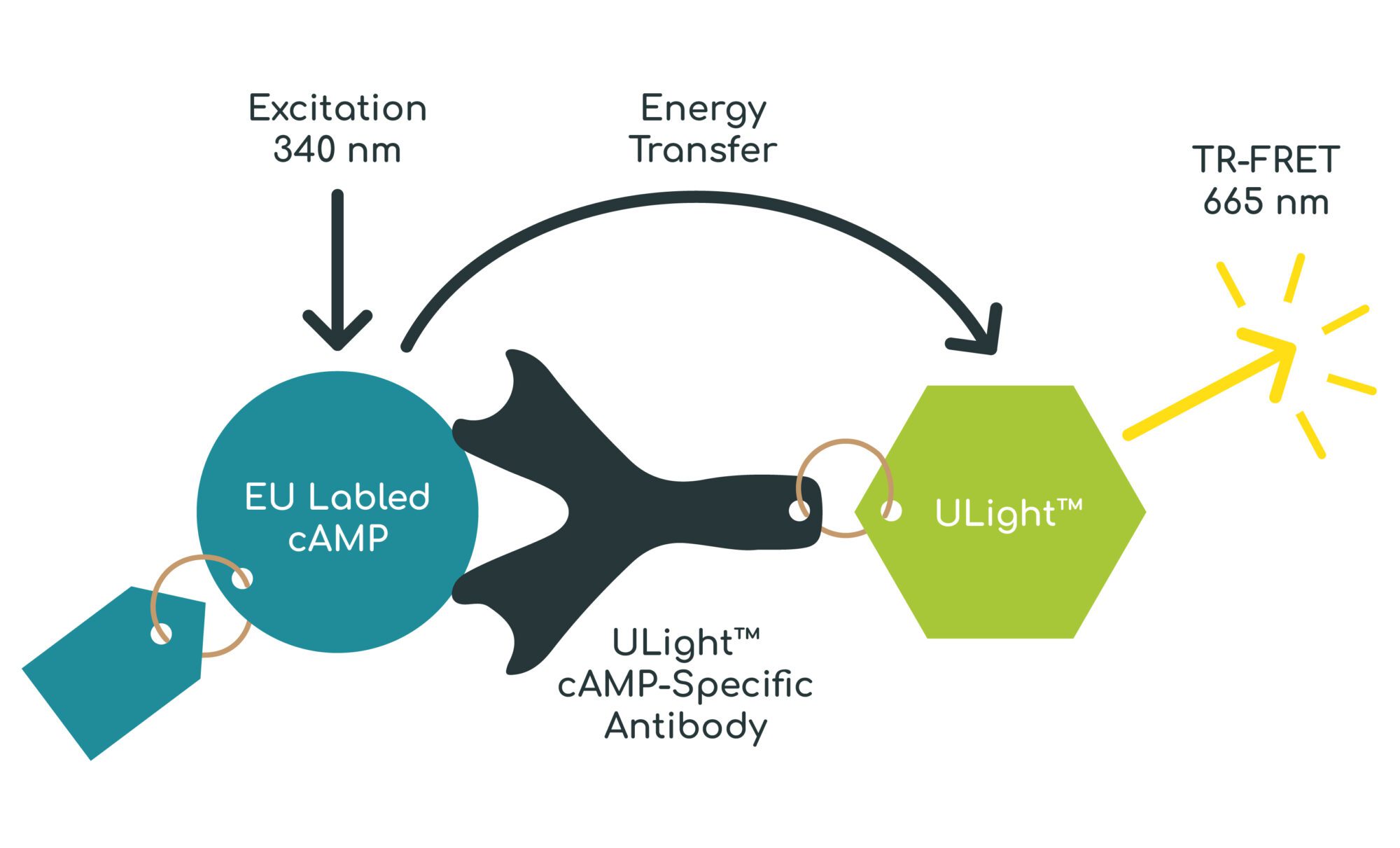
cAMP assays are used to measure activation of GPCRs coupled to Gs and Gi/o. Activation of GPCRs coupled to Gs results in adenylyl cyclase stimulation and increased production of the second messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Conversely, activation of GPCRs coupled to Gi/o results in a reduction of cAMP production. cAMP levels are measured using a TR-FRET based assay.
Calcium flux assays can be used to measure activation or inhibition of GPCR signalling by monitoring intracellular calcium levels, and is useful for investigating GPCRs coupled to Gq/11.
Calcium Flux Assay
Cells are loaded with a fluorescent dye such as Fluo-8, then stimulated with an agonist, leading to increased intracellular calcium levels. Upon binding to calcium, the fluorescence of the dye is enhanced.
Kinase assays are used to measure the effect of test compounds such as inhibitors for potential cancer treatment upon kinase activity. A range of concentrations of the test compound are incubated with the kinase. ADP formed by the kinase is measured using a fluorescent read-out, providing information on the IC50.
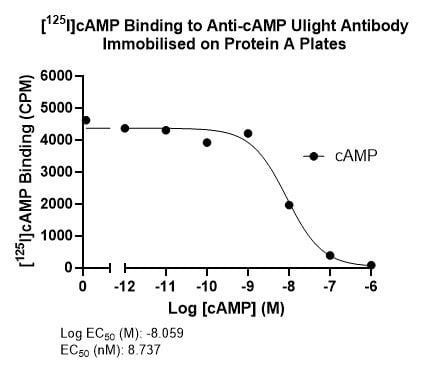
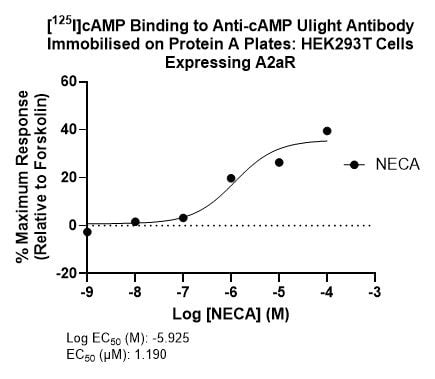
Example Data: Radioimmunoassay
Displacement of [125I]cAMP (custom labelled in-house) bound to anti-cAMP antibody immobilized onto protein A plates with unlabelled cAMP. EC50 = 8.737 nM (left). Displacement of [125I]cAMP bound to anti-cAMP antibody immobilized onto protein A plates with cAMP produced by HEK293T cells transfected with A2aR and treated with increasing concentrations of NECA. EC50 = 1.190 µM (right). Several selective A2aR agonists are currently being investigated for the treatment of sickle cell anemia and pulmonary inflammation.
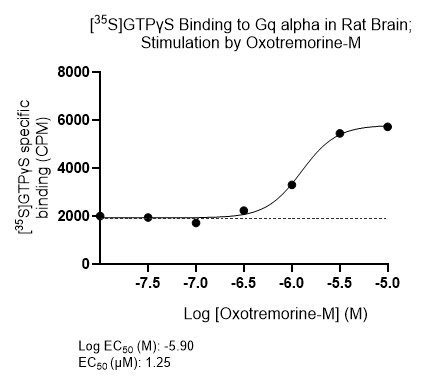
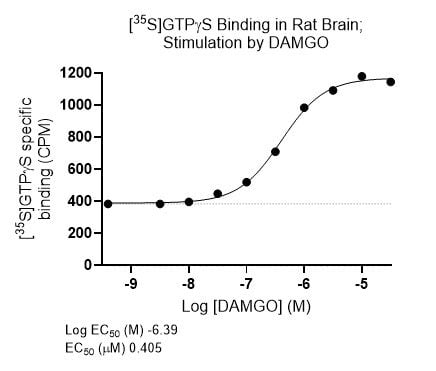
Example Data: GTPγS Stimulation Assay
Oxotremorine-M is a selective muscarinic acetylcholine agonist that induces tremors characteristic of Parkinson’s disease, making it a useful tool to screen for anticholinergic drugs that antagonize this effect as potential treatments. Stimulation of [35S]GTPγS binding assay in rat brain with post-hoc immunopreciptation step to selectively measure Oxotremorine-M-stimulated binding to Gq alpha (M2/M4 receptors), EC50 = 1.25 µM (left).
DAMGO is a mu receptor agonist utilized in studies investigating tolerance and dependence. Stimulation of [35S]GTPγS binding in rat brain striatum by DAMGO, EC50 = 0.405 µM (right).
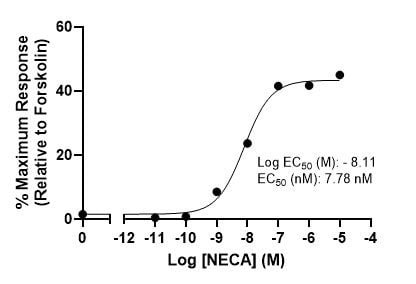
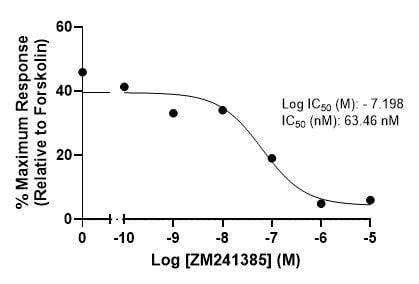
Example Data: cAMP Agonist and Antagonist Assay
Stimulation of cAMP production by NECA in CHO K1 cells transiently transfected to express human adenosine 2a receptors, EC50 = 7.78 nM (left). Inhibition of NECA-stimulated cAMP production by ZM241385 in HEK293T cells transiently transfected to express human A2aR, IC50 = 63.46 nM (right). A2aR antagonists are a potential treatment for Parkinson’s disease and cancers.