ELISAs
Additional Service
as part of a core receptor pharmacology study
Our ELISA service provides additional information to that obtained in our radioligand binding assays. ELISAs detect a target antigen in a range of sample types including plasma, tissue homogenate and cell lysate. We perform this service in 96-well plates, either using commercially available ELISA kits for common targets, or building a bespoke assay to suit customer requirements.
We use this technique to:
- confirm the expression of the target protein in transfected or stable cell lines;
- screen a range of samples for the presence of the target of interest;
- compare levels of target antigen expression in treated or untreated tissue;
- characterize the effects of an inhibitor (competitive ELISAs).
ELISAs provide qualitative information to confirm the presence or absence of a target protein within a sample, compared to a blank or control antigen. We obtain semi-quantitative data as an indication of relative levels of antigen in test samples, where the absorbance signal is dependent upon the level of target in the sample. We can also run quantitative ELISAs, where precise concentrations of antigen can be determined by comparing absorbance signals to that of a standard curve run with a protein of a known concentration.
ELISAs can be carried out using direct, indirect and sandwich approaches:
In a direct ELISA, we immobilize the target antigen directly to the assay plate, then bind an antibody specific for the target. This antibody is coupled to a reporter enzyme. Substrate is added and a coloured reaction product generated. The absorbance of the wells are read after terminating the reaction.
In an indirect ELISA, we immobilize the target antigen directly to the assay plate, then bind a primary antibody specific for the target antigen. This is followed by binding of a secondary antibody coupled to a reporter enzyme. Substrate is then added resulting in a colorimetric readout.
In a sandwich ELISA, we use matched-antibody pairs (two antibodies that bind to two different epitopes on the target protein). The first antibody (capture antibody) is precoated onto the ELISA plate and immobilises the target antigen present in the sample. Any unbound antigen is then washed off, and the second matched pair antibody is incubated in the wells. This antibody is either conjugated to a reporter enzyme, or after an additional wash to remove unbound antibody, bound by a third antibody conjugated to a reporter enzyme. After a final wash step to remove unbound antibody, the wells are incubated with a substrate. The reaction is terminated, and the absorbance of the wells read.
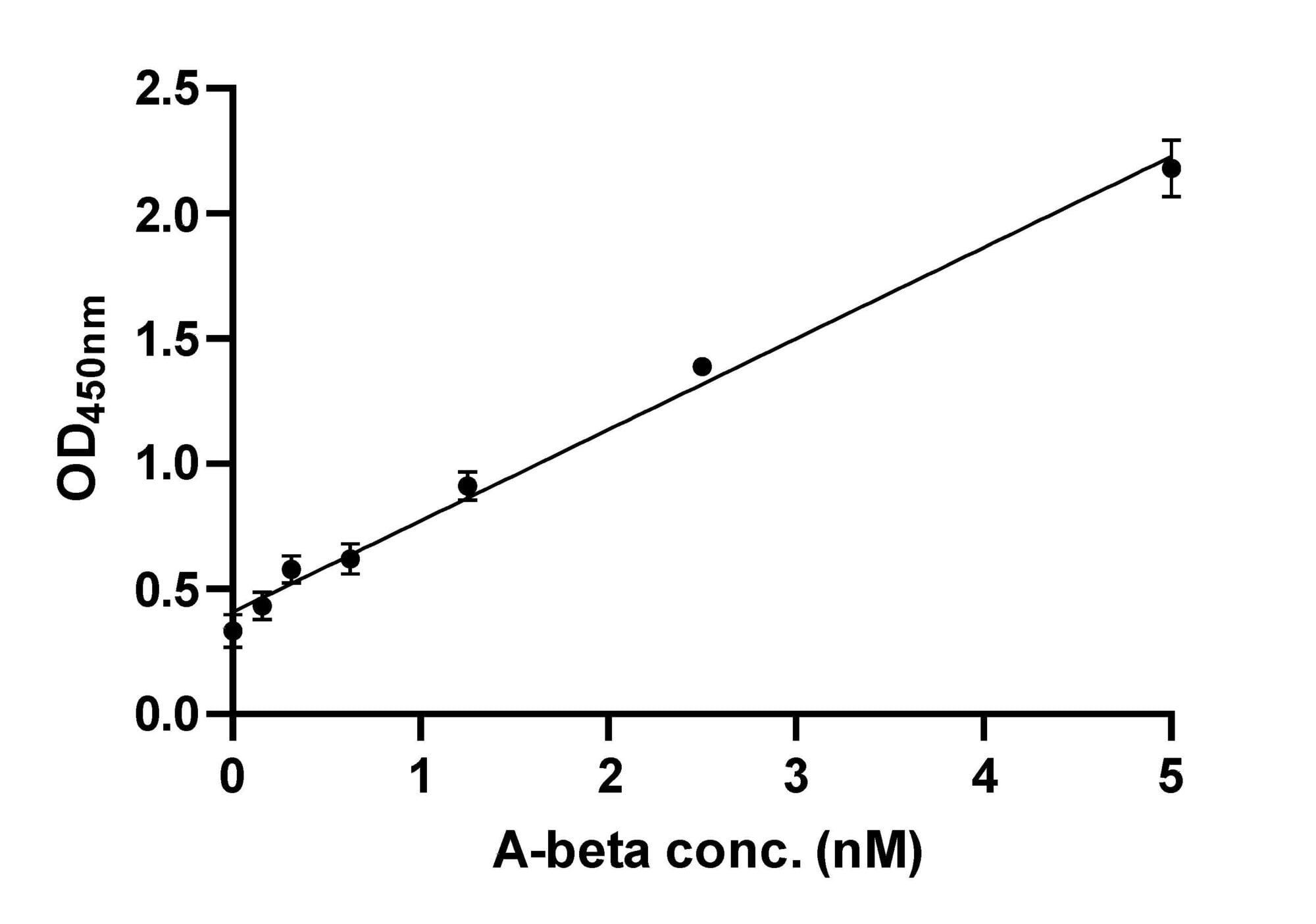
Example Data: Indirect ELISA
Dilution series generated for A-beta fibrils using an indirect ELISA. Limit of detection (LOD) = 0.53 nM. Limit of quantitation (LOQ) = 1.78 nM. LOD = 3σ/s and LOQ = 10σ/s, where σ is the standard deviation of the blanks and s is the slope.

Example Data: Sandwich ELISA
Sandwich ELISA for serially diluted phospho-Akt (Ser473) standard using a Cell Signaling Technology FastScan™ kit. Limit of detection (LOD) = 0.183 µg. Limit of quantitation (LOQ) = 0.611 µg. LOD = 3σ/s and LOQ = 10σ/s, where σ is the standard deviation of the blanks and s is the slope.



