Cellular Uptake
& Release
Cellular uptake assays and cellular release assays use live cells to examine the effects of compounds on receptor or transporter systems. They can determine a compound’s potency and efficacy. They can also be used to measure a compound’s transport into cells or efflux from cells. Our cell-based studies are conducted on either primary or immortalized cells lines. Cell culture is undertaken by us.
Cellular uptake assays can be used to measure the transport or internalization of labeled compounds into cells or the potency of unlabeled test compounds in inhibiting this transport. Labeled substances can be neurotransmitters, metabolites, drugs or proteins.
Applications include:
- Determination of IC50 values for test compounds against cellular uptake of radiolabeled neurotransmitters.
- Determination of IC50 values for test compounds against uptake of tritium or 14C-labeled metabolites or drugs.
- Cellular uptake and internalization of 125I-labeled proteins.
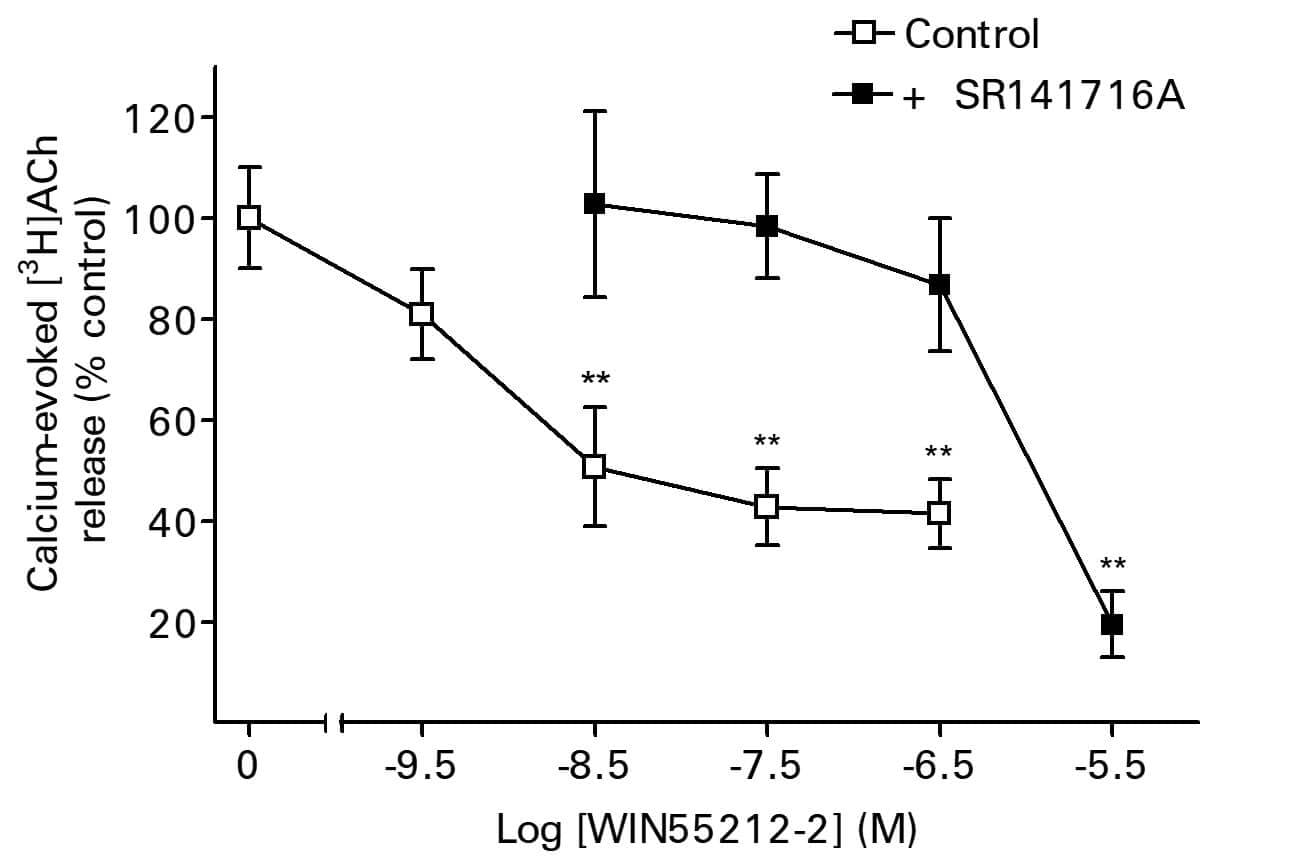
Cellular release assays can be used to quantify the efflux of labeled substances from cells. Efflux can be via membrane ion channels, membrane transport or from cell lysis.
Applications include:
- 86Rb+ rubidium efflux assay for quantification of drug effects on stimulation or inhibition of ligand-gated ion channel activity (nicotinic).
- Efflux of 3H and 125I-labeled drugs from cells via transport.
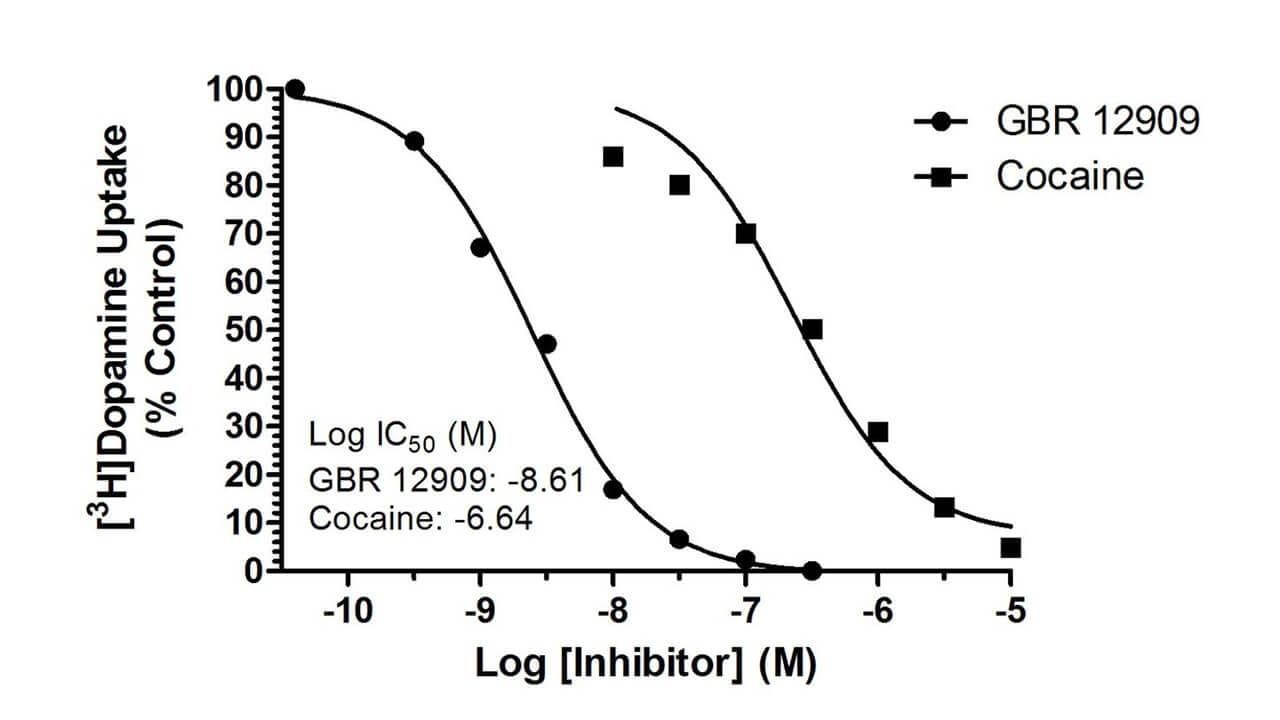
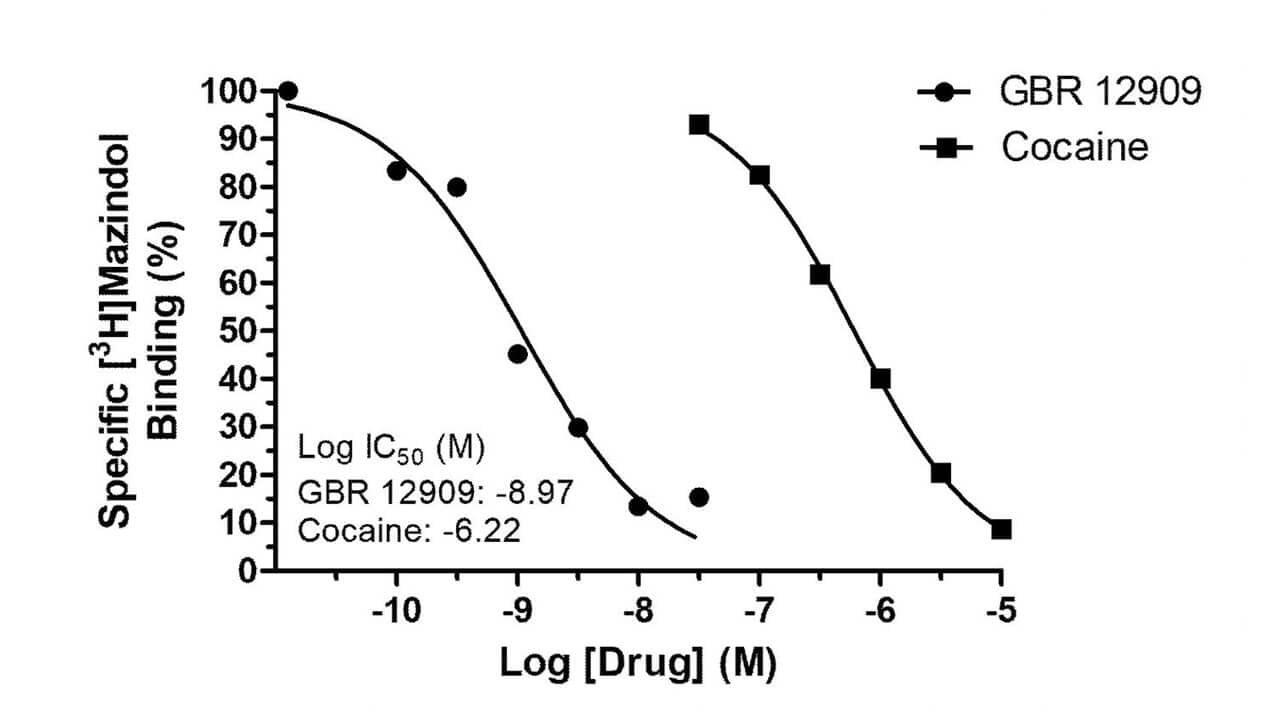
Example Data: Cellular Uptake Assay
Inhibition of [3H]dopamine uptake into rat brain synaptosomes by the dopamine transport inhibitors, GBR 12909 and cocaine (left), shown in comparison with inhibition of [3H]mazindol binding (right).